[vc_row full_width=”stretch_row” el_class=”what_secA” css=”.vc_custom_1681532822540{background-color: #ecf8fd !important;background-position: center !important;background-repeat: no-repeat !important;background-size: cover !important;}”][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]
The Employee Retention Credit
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]
ERC is a stimulus program designed to help those
businesses that were able to retain their employees
during the Covid-19 pandemic.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][vc_column width=”1/2″][vc_single_image image=”212″ img_size=”full”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row full_width=”stretch_row_content_no_spaces” el_class=”what_va” css=”.vc_custom_1681533137216{background-image: url(https://ercprofessionalgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/what-va.png?id=504) !important;background-position: center !important;background-repeat: no-repeat !important;background-size: cover !important;}”][vc_column][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row full_width=”stretch_row_content” disable_element=”yes” el_class=”what_secB”][vc_column][vc_single_image image=”216″ img_size=”full” alignment=”right”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row el_class=”what_secC”][vc_column][vc_column_text]
A Guide For Claiming the Employee Retention Credit
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]Enacted under the CARES Act to subsidize businesses which retained workers employed during the pandemic, the Employee Retention Credit (ERC) is a refundable payroll tax credit available to businesses which experienced a significant decline in its gross receipts during the pandemic or whose operations were subject to a full or partial suspension because of a governmental order.[/vc_column_text][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_column_text]Establishing eligibility by satisfying the business operations suspension test can be a treacherous journey, watches replicabut the payoff can be tremendous.best replica watches Complicated business scenarios add uncertainty and with guidance lacking, fake Rolexit is important that a prudent business owner consult an cheap rolex replicaERC expert with substantial experience navigating the business operations suspension rules because they often require a complex analysis with many moving parts.replica watches for sale[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_single_image image=”223″ img_size=”full”][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_column_text]The amount of the credit is based on a percentage of “qualified wages”, which can include allocable qualified health plan premiums paid by the employer.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row el_class=”what_secD sum”][vc_column][vc_tta_tabs active_section=”1″][vc_tta_section title=”ERC Step-by-Step Analysis” tab_id=”1680346353214-536945c6-1df5″][vc_column_text]
ERC Step-by-Step Analysis
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]
Applicable to 2020 (6/30/20, 9/30/20, 12/31/20) and 2021 (3/31/21, 6/30/21, 9/30/21) quarters
(12/31/21 is eligible as well but only for a recovery start-up business as defined in section
3134(c)(5) of the Internal Revenue Code).
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]
-
1
-
Aggregation Rules
[/vc_column_text][vc_row_inner el_class=”what_tabA”][vc_column_inner][vc_column_text]
If the Aggregation Rules apply, you must combine the employees and the gross receipts of each business in applying the ERC rules.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]

Does the business owner (individual) own more than 80% of another business?
If Yes, combine businesses and proceed to Step 2.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]

Does the business itself own more than 80% of another business?
If Yes, combine businesses and proceed to Step 2.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]

Does the business or any aggregated business from above have an interest in a partnership or corporation which regularly performs services for the business?
If Yes, combine businesses and proceed to Step 2.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_column_text]
-
2
-
Basic Qualifying Rules (Trade or Business)
[/vc_column_text][vc_row_inner el_class=”what_tabA sub”][vc_column_inner][vc_column_text]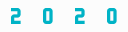
Did the employer carry on a “trade or business” during the year?
If Yes, proceed to Step 3. If No, ERC unavailable.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]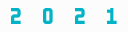
Did the employer carry on a “trade or business” in the quarter under consideration? For 2021, exclude if the employer is part of a Federal or State agency unless the employer is a college, university or medical facility or hospital.
If Yes, proceed to Step 3. If No, ERC unavailable.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_column_text]
-
3
-
Revenue Test
[/vc_column_text][vc_row_inner el_class=”what_tabA”][vc_column_inner][vc_column_text]
Reminder, if businesses are aggregated above (see Step 1), all the businesses are treated as a single employer for purposes of determining whether the employer experienced a significant decline in gross receipts.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]
Generally, gross receipts for the quarter must be less than 50% of the gross receipts for the same quarter in 2019 (with more expansive rules which apply for the quarter ended 09/30/20 and 12/31/20 by allowing for alternative quarter comparisons for qualification).
If Revenue Test met, proceed to Step 5. If not, proceed to Step 4.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]
Generally, gross receipts for the quarter must be less than 80% of the gross receipts for the same quarter in 2019 (unless the employer was not in existence during all or part of the quarters during 2019 in which case certain adjustments are permitted).
If Revenue Test met, proceed to Step 5. If not, proceed to Step 4.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]
Special rules regarding the determination of gross receipts are considered if the employer is a 501(c) organization under IRC section 6033.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_column_text]
-
4
-
Suspension of Business Test
[/vc_column_text][vc_row_inner el_class=”what_tabA”][vc_column_inner][vc_column_text]
Reminder, if businesses are aggregated above (see Step 1), each business is tested separately below so that if one of the businesses is impacted, all are deemed impacted.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]

Was there a GOVERNMENT ORDER that applied and limited the business or its supplier’s travel in commerce?
If Yes, go to B. If No, not eligible for ERC.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]
Supplier Impact: Were the operations of the business supplier suspended so that the business itself failed to receive critical goods and/or service?
If Yes, eligible for ERC. If No, go to C.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]

Business impact: Are all the business operations considered Non-Essential?
ex: The premises were closed
If No, go to D. If Yes, then proceed below:
[/vc_column_text][vc_raw_html]JTNDZGl2JTIwY2xhc3MlM0QlMjJ3aGF0X21haW4lMjBDJTIyJTNFJTBBJTNDZGl2JTNFJTNDaSUyMGNsYXNzJTNEJTIyZmElMjBmYS1jaGVjayUyMiUyMGFyaWEtaGlkZGVuJTNEJTIydHJ1ZSUyMiUzRSUzQyUyRmklM0UlM0MlMkZkaXYlM0UlMEElM0NkaXYlM0UlMEElM0NoNCUzRSUzQ3N0cm9uZyUzRUZ1bGwlMjBTdXNwZW5zaW9uJTIwJTI4YnVzaW5lc3MlMjBjbG9zZWQlMjklM0ElMjAlM0MlMkZzdHJvbmclM0UlMjBDb3VsZCUyMHRoZSUyMGJ1c2luZXNzJTIwY29udGludWUlMjB0byUyMG9wZXJhdGUlMjBpbiUyMGElMjBjb21wYXJhYmxlJTIwbWFubmVyJTIwdXNpbmclMjBUZWxld29yayUzRiUzQyUyRmg0JTNFJTBBJTNDcCUzRUZvciUyMGElMjBkZXNjcmlwdGlvbiUyMG9mJTIwJUUyJTgwJTlDY29tcGFyYWJsZSUyMG1hbm5lciUyQyVFMiU4MCU5RCUyMHNlZSUzQSUyME5vdGljZSUyMDIwMjEtMjAlMjBhbmQlMjBjb25zaWRlciUyMGVtcGxveWVyLWJ1c2luZXNzJUUyJTgwJTk5cyUyMGFiaWxpdHklMjB0byUyMHRyYW5zaXRpb24uJTNDYnIlM0VJZiUyMFllcyUyQyUyMGJ1c2luZXNzJTIwaXMlMjBub3QlMjBlbGlnaWJsZSUyMGZvciUyMEVSQy4lMjBJZiUyME5vJTJDJTIwZWxpZ2libGUlMjBmb3IlMjBFUkMuJTNDJTJGcCUzRSUwQSUzQyUyRmRpdiUzRSUwQSUzQyUyRmRpdiUzRQ==[/vc_raw_html][vc_raw_html]JTNDZGl2JTIwY2xhc3MlM0QlMjJ3aGF0X21haW4lMjBDJTIyJTNFJTBBJTNDZGl2JTNFJTNDaSUyMGNsYXNzJTNEJTIyZmElMjBmYS1jaGVjayUyMiUyMGFyaWEtaGlkZGVuJTNEJTIydHJ1ZSUyMiUzRSUzQyUyRmklM0UlM0MlMkZkaXYlM0UlMEElM0NkaXYlM0UlMEElM0NoNCUzRSUzQ3N0cm9uZyUzRVBhcnRpYWwlMjBTdXNwZW5zaW9uJTIwJTI4YnVzaW5lc3MlMjByZW9wZW5pbmclMjklM0ElMjAlM0MlMkZzdHJvbmclM0UlMjAlMjBEaWQlMjB0aGUlMjBnb3Zlcm5tZW50JTIwb3JkZXJzJTIwaW1wYWN0JTIwdGhlJTIwYnVzaW5lc3MlMjBuZWdhdGl2ZWx5JTIwaW4lMjBtb3JlJTIwdGhhbiUyMGElMjBub21pbmFsJTIwd2F5JTNGJTNDJTJGaDQlM0UlMEElM0NwJTNFZXglM0ElMjBXYXMlMjB0aGVyZSUyMGElMjByZWR1Y3Rpb24lMjBpbiUyMHRoZSUyMGFiaWxpdHklMjB0byUyMHByb2R1Y2UlMjBnb29kcyUyMG9yJTIwcHJvdmlkZSUyMHNlcnZpY2VzJTNGJTNDYnIlM0VJZiUyMFllcyUyQyUyMGVsaWdpYmxlJTIwZm9yJTIwRVJDLiUyMElmJTIwTm8lMkMlMjBidXNpbmVzcyUyMGlzJTIwbm90JTIwZWxpZ2libGUlMjBmb3IlMjBFUkMuJTNDJTJGcCUzRSUwQSUzQyUyRmRpdiUzRSUwQSUzQyUyRmRpdiUzRQ==[/vc_raw_html][vc_column_text]
Are all or some of the business operations considered Essential?
ex: The premises remained open or only some parts of operations were closed
[/vc_column_text][vc_raw_html]JTNDZGl2JTIwY2xhc3MlM0QlMjJ3aGF0X21haW4lMjBDJTIyJTNFJTBBJTNDZGl2JTNFJTNDaSUyMGNsYXNzJTNEJTIyZmElMjBmYS1jaGVjayUyMiUyMGFyaWEtaGlkZGVuJTNEJTIydHJ1ZSUyMiUzRSUzQyUyRmklM0UlM0MlMkZkaXYlM0UlMEElM0NkaXYlM0UlMEElM0NoNCUzRUlmJTIwJTNDc3Ryb25nJTNFQUxMJTNBJTNDJTJGc3Ryb25nJTNFJTIwJTIwVGhlJTIwYnVzaW5lc3MlMjBtdXN0JTIwc2hvdyUyMHRoYXQlMjB0aGUlMjBnb3Zlcm5tZW50JTIwb3JkZXIlMjBjYXVzZWQlMjBhJTIwcmVkdWN0aW9uJTIwaW4lMjBpdHMlMjBncm9zcyUyMHJlY2VpcHRzJTIwJTI4d2hlbiUyMGNvbXBhcmVkJTIwdG8lMjB3aGF0JTIwdGhlJTIwZ3Jvc3MlMjByZWNlaXB0cyUyMGNvdWxkJTIwaGF2ZSUyMGJlZW4lMjB3aXRob3V0JTIwdGhlJTIwZ292ZXJubWVudCUyMG9yZGVyJTI5JTIwb3IlMjBpbmNyZWFzZSUyMGluJTIwbGFib3IlMjBjb3N0cyUyMGJ5JTIwbW9yZSUyMHRoYW4lMjBhJTIwJUUyJTgwJTlDbm9taW5hbCVFMiU4MCU5RCUyMGFtb3VudCUyMCUyODEwJTI1JTI5LiUzQyUyRmg0JTNFJTBBJTNDJTJGZGl2JTNFJTBBJTNDJTJGZGl2JTNF[/vc_raw_html][vc_raw_html]JTNDZGl2JTIwY2xhc3MlM0QlMjJ3aGF0X21haW4lMjBDJTIyJTNFJTBBJTNDZGl2JTNFJTNDaSUyMGNsYXNzJTNEJTIyZmElMjBmYS1jaGVjayUyMiUyMGFyaWEtaGlkZGVuJTNEJTIydHJ1ZSUyMiUzRSUzQyUyRmklM0UlM0MlMkZkaXYlM0UlMEElM0NkaXYlM0UlMEElM0NoNCUzRUlmJTIwJTNDc3Ryb25nJTNFU09NRSUzQyUyRnN0cm9uZyUzRSUyMCUyOGJ1c2luZXNzJTIwcHJlbWlzZXMlMjByZW1haW5lZCUyMG9wZW4lMjBmb3IlMjBlc3NlbnRpYWwlMjBwdXJwb3NlcyUyMGJ1dCUyMG90aGVyJTIwcGFydHMlMjBvZiUyMGJ1c2luZXNzJTIwd2VyZSUyMHN1c3BlbmRlZCUyOSUzQSUyMFdhcyUyMHRoZSUyMGRpc2NvbnRpbnVlZCUyMGJ1c2luZXNzJTIwb3BlcmF0aW9ucyUyMCUyOG5vbi1lc3NlbnRpYWwlMjklMjBjb21wb25lbnQlMjBtb3JlJTIwdGhhbiUyMGElMjBub21pbmFsJTIwcGFydCUyMG9mJTIwdGhlJTIwYnVzaW5lc3MlMjBvcGVyYXRpb25zJTIwJTI4MTAlMjUlMjklM0YlM0MlMkZoNCUzRSUwQSUzQyUyRmRpdiUzRSUwQSUzQyUyRmRpdiUzRQ==[/vc_raw_html][vc_raw_html]JTNDZGl2JTIwY2xhc3MlM0QlMjJ3aGF0X21haW4lMjBEJTIyJTNFJTBBJTNDZGl2JTNFJTNDaW1nJTIwc3JjJTNEJTIyJTJGd3AtY29udGVudCUyRnVwbG9hZHMlMkYyMDIzJTJGMDQlMkZjaGF0LXF1ZXN0aW9uLnBuZyUyMiUyMGFsdCUzRCUyMmNoYXQtcXVlc3Rpb24lMjIlM0UlM0MlMkZkaXYlM0UlMEElM0NkaXYlM0UlMEElM0NoNCUzRUlmJTIwJTNDc3Ryb25nJTNFWUVTJTJDJTNDJTJGc3Ryb25nJTNFJTIwd2VyZSUyMHRoZSUyMGRpc2NvbnRpbnVlZCUyMG9wZXJhdGlvbnMlMjBhYmxlJTIwdG8lMjBwZXJmb3JtJTIwaW4lMjBhJTIwY29tcGFyYWJsZSUyMG1hbm5lciUyMHZpYSUyMFRlbGV3b3JrJTNGJTNDJTJGaDQlM0UlMEElM0NwJTNFSWYlMjBObyUyQyUyMGJ1c2luZXNzJTIwaXMlMjBlbGlnaWJsZSUyMGZvciUyMEVSQyUyMGFuZCUyMGFwcGx5JTIwMTAlMjUlMjB0ZXN0JTIwYmVsb3cuJTIwSWYlMjBZZXMlMkMlMjBhcHBseSUyMDEwJTI1JTIwdGVzdCUyMGJlbG93LiUzQyUyRnAlM0UlMEElM0MlMkZkaXYlM0UlMEElM0MlMkZkaXYlM0U=[/vc_raw_html][vc_column_text]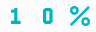
10% Test: Did the government order restrict continuing business operations (essential operations) such that gross receipts were reduced by more than 10%?
OR did additional work necessitated by government orders increase labor costs by more than 10%?
If No, Failed Test and not eligible for ERC. If Yes, eligible for ERC.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_column_text]
-
5
-
ERC Calculation
[/vc_column_text][vc_row_inner el_class=”what_tabA”][vc_column_inner][vc_column_text]
If the business passed the Revenue Test (step 3), all wages become eligible for that quarter in which the Revenue Test was met. If the business passed the Suspension of Business Test (step 4), all wages become eligible for that quarter in which the suspension occurred.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]
Wages eligible above can only be used if paid or accrued for services rendered during the quarter and then for:
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]
The refundable tax credit is 50% of up to $10,000 in wages paid per employee from 3/12/20 to 12/31/20 by an eligible employer for a total of $5,000 per employee for 2020.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]
The refundable tax credit is 70% of wages paid per employee during the quarter ending 3/31/21, 6/30/21 and 9/30/21, not to exceed $7,000 per quarter.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]
However, if the business is a “Large Employer,” then only if the wages are paid to employees who were not providing services due to a decline in revenue or suspension of business and even then, only for wages which are paid for working an equivalent duration during the 30 days immediately preceding the period in which the qualified wages are paid or incurred.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]
06/30/20, 9/30/20 and 12/31/20, if on average business had more than 100 full-time employees in 2019.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]
3/31/21, 6/30/21, and 9/30/21, if on average business had more than 500 full-time employees in 2019.
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]
Note: Include Group Health Plan expenses if there was coverage for the quarter in question
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]
Certain wages are excluded:
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]
Related employees (owner, owner’s parent, children and siblings)
-
OR
-
PPP Forgiveness with respect to the wages paid
-
OR
-
Wages counted under Family First Coronavirus Act
-
OR
-
Wages paid under Family Leave Credit
-
OR
-
If Employer received credits under IRC sections 41 (Qualified Research), 45A (Indian Employment Credit), 45P (Active Duty Members), 51 (Work Opportunity Credit) or 1396 (Empowerment Zone).
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_tta_section][vc_tta_section title=”ERC Summary Rules” tab_id=”1680346347948-f8e590b8-1ee2″][vc_row_inner el_class=”sum-rules”][vc_column_inner][vc_column_text]
ERC Summary Rules
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]
Each quarter should be considered separately. This chart offers a simple illustration of the differences in
the rules for each quarter:
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]
| Eligibility Period | 3/13/20 – 12/31/20 | 2021 – Q1 & Q2 | 2021 – Q3 | 2021 – Q4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eligible Employers | Any employer operating a trade or business, including tax-exempt organizations. | Expanded to include certain governmental employers, colleges and universities | N/A | |
| Qualified Wages | $10,000 per employee for the year. | $10,000 per employee per calendar quarter | N/A | |
| Credit per Employee | 50% of Qualified Wages – Maximum of $5,000 per employee in 2020 | 70% of Qualified Wages – Maximum of $7,000 per employee per quarter (Q1, Q2, and Q3 in 2021) | N/A | |
| Eligible Small Employer1 | Averaged 100 or fewer full-time employees in 2019 | Averaged 500 or fewer full-time employees in 2019 | N/A | |
| Eligibility Requirements: Full or Partial Suspension | Full or partial suspension of operations due to Covid-19 related government order during any quarter | N/A | ||
| Eligibility Requirements: Decline in Gross Receipts | Greater than 50% v. the same quarter in 2019 | Greater than 20% v. the same quarter in 2019 | N/A | |
| Eligibility Requirements: Severely Financially Distressed Employer | Not applicable in 2020 | Not applicable in Q1 or Q2 of 2021 | Gross receipts decline by greater than 90% – may treat all wages paid during Q3 of 2021 as qualified wages | N/A |
| Recovery Start-up Business | Not applicable | Not applicable in Q1 or Q2 of 2021 | New category of trade or business that started after 2/15/2020 and had $1 million or less in average annual gross receipts for the 3-taxable-year period ending with the taxable year that precedes the calendar quarter for which the credit is determined.
Credit limited to $50,000 per quarter (Q3 and Q4) |
|
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text]
1 Eligible Small Employers and Severely Financially Distressed Employers may treat all wages paid to all employees as qualified wages. For all other eligible employers, wages are limited to amounts paid to employees during the period of time the employees are not providing services (e.g., on account of a suspension of operations).
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_tta_section][/vc_tta_tabs][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row full_width=”stretch_row_content_no_spaces” el_class=”what-vb” css=”.vc_custom_1681533920445{background-image: url(https://ercprofessionalgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/what-vb.png?id=506) !important;background-position: center !important;background-repeat: no-repeat !important;background-size: cover !important;}”][vc_column el_class=”contact_form”][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row full_width=”stretch_row” css=”.vc_custom_1681533861340{background-color: #ecf8fd !important;background-position: center !important;background-repeat: no-repeat !important;background-size: cover !important;}” el_class=”what_secf”][vc_column][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner][vc_column_text]
Can businesses which received Paycheck Protection Program (“PPP”) loan(s) qualify for the ERC?
Yes, although initially an employer was required to choose between a PPP loan or the ERC, the Taxpayer Certainty and Disaster Tax Relief Act of 2020 eliminated this restriction allowing eligible businesses to claim the ERC even though they received one or more PPP loan so long as none of the qualified wages were paid using PPP loans which were forgiven.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner][vc_column_text]
Can a non-profit business claim the ERC?
Yes, a 501(c) non-governmental tax-exempt organization can qualify for the ERC.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_column_text]
Have more questions?
Checkout Our FAQs Page
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row el_class=”what_secG” el_id=”free-erc-evaluation”][vc_column el_class=”contact_form”][vc_column_text]
Get a Free ERC Evaluation
[/vc_column_text][vc_column_text][contact-form-7 id=”314″ title=”Contact form 1″][/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]




